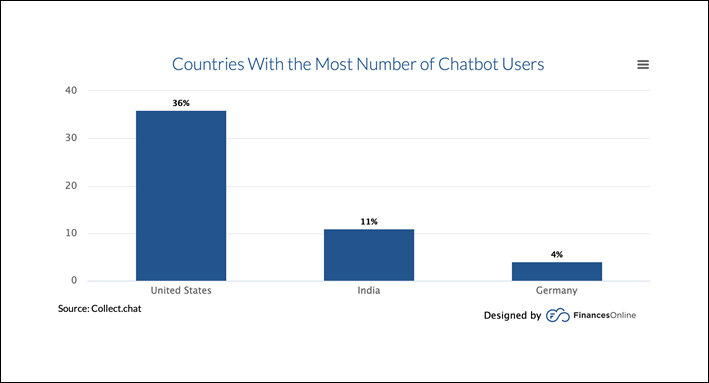
It is assumed that 1.4 billion people are using chatbots, with top 5- countries being the United States and India.
Interactive Voice Responses (IVR) was the key term in early 2000’s where back offices had business process outsourcing units (BPO’s) mushrooming in developing nations. The key was to learn and neutralize accents (American and British), to support various companies.
Scores of hours and metrics used to go in calculating wait time of customers, call resolution times and many other aspects. I remember, when I joined my first job where I miserably failed in rolling my R’s! Cut to 2023, I am writing an article which is the stark opposite of the industry that was dominating the Indian and other skylines in the 2000’s.
Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing customer service chatbots are a norm. Customer facing representatives are the last resort. They have grown to be conversational agents using generative AI moving away from basic evolutionary chatbots responding to basic questions, but can now predict questions.
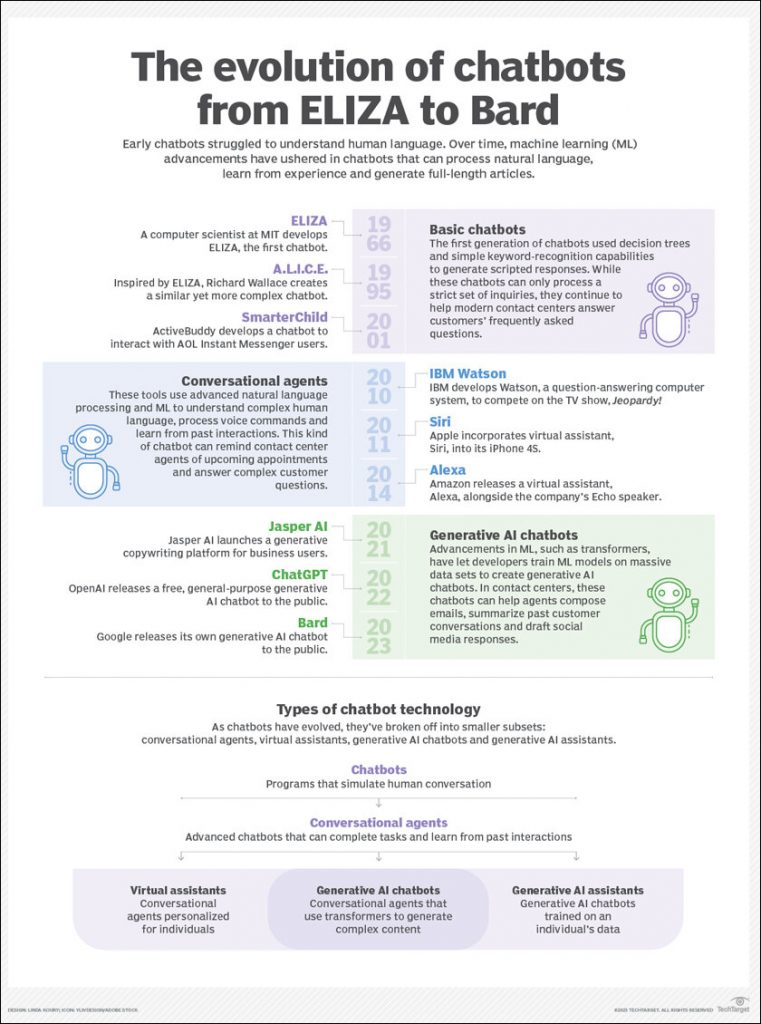
The picture below depicts the interesting journey from basic Chatbots to Bard. Humans had an extension of interacting with computers using a keyboard and evolved in H1960s when Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, the world’s first chatbot. Machine learning (ML), however, now can understand complex language, learn from past interactions and generate creative content.
From Frustrating to Fantastic!
I was struggling to figure out where one of my deliveries on Amazon were, when I went to the chatbot.
All it asked me was the ‘order’ I was talking about and it actually tracked the delivery, where it gave me options to check on ‘where is my delivery?’, after three futile attempts of actually tracking the parcel, it intuitively passed me on to customer support as we were not getting anywhere.
Cut to a month later a similar problem occurred, where the chatbot was able to resolve a similar problem without customer support intervention!
Far from frustrating users, generative AI produces various types of content, including text, imagery, audio and synthetic data. The interactive user interfaces and the penchant for creating high-quality text, graphics and videos in a short span of time makes it a likable and fantastic option.
Evolution of Chatbots
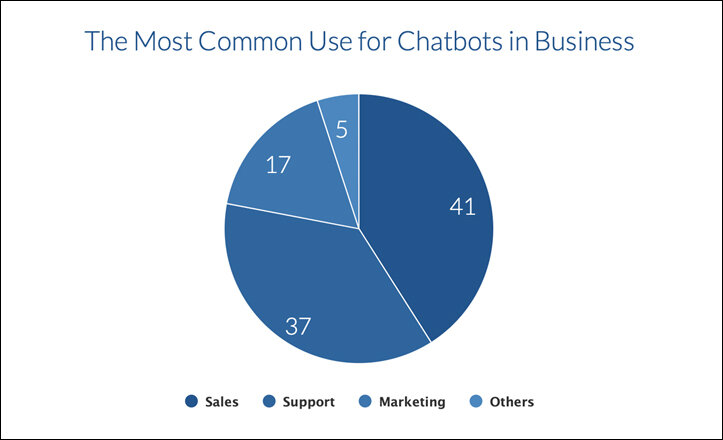
| Basic Chatbots | Conversational Chatbots | Generative AI Chatbots |
| Basic chatbots started with ELIZA and developed into ALICE which is a smarter child. They use basic algorithms and detect keywords and offer predetermined responses. | In early 2010s, Machine learning picked up and conversational agents started ruling the markets. Natural Language PRocessing and machine learning was added to include voice recognition and providing options and created a new generation of virtual assistants. | Transformer neural networks and large language models (LLMs) have given rise to Jasper AI, ChatGPT and Bard. This technology can give predictive text, compose messages, provide comprehensive and customer specific responses |
| Lacks Natural Language Processing | Lacks learning and provides predetermined contextual responses | Depends on the large data sets and can be manipulated based on the data sets |
| Used in providing customers with pre-defined information e.g. order status, store address, etc. | IBM Watson, Siri and Alexa can detect mood and set up appointments, place order, etc. | ChatGPT, Bard can compose essays and articles like these in matter of seconds. |
What is the difference between a Chatbot and a Virtual Assistant?
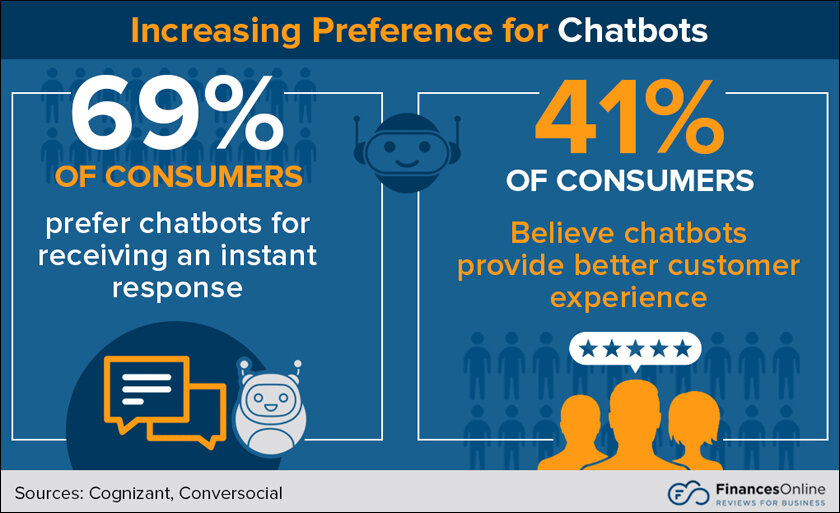
The scale of support is the primary differentiator for virtual assistants and Chatbots. There is an exponential increase in the personal assistance that virtual assistants provide in comparison with chatbots.
Over 68% respondents in a survey preferred chatbots to prevent interaction with humans for basic information like balance on an account, recommendations, etc.
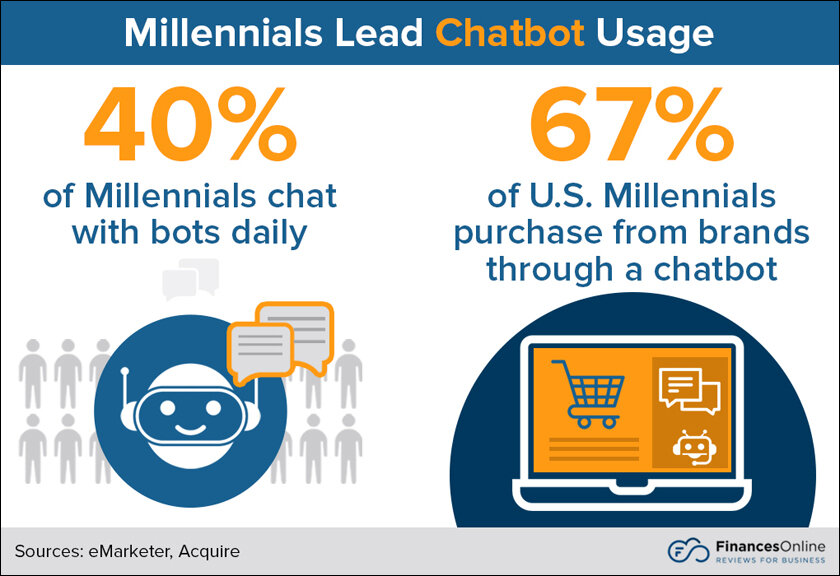
Chatbots
| Pattern matches | Natural language understanding (NLU) | Natural language processing (NLP) |
| Answer any messages or voice, bots use pattern matches to the group then it delivers an appropriate response | algorithm based bot that examines the sentence and it doesn’t have any historical contexts of the user conversation. It means if it gets a response to a question, it is asked recently, it will not recall any query. | Bot that uses natural language processing (NLP) method to convert the voice or text into structured data. To complete the entire process it goes through a series of steps, such as tokenizations, analysis sentiment, normalization, name recognition, and dependency parsing. |
What does the future look like?
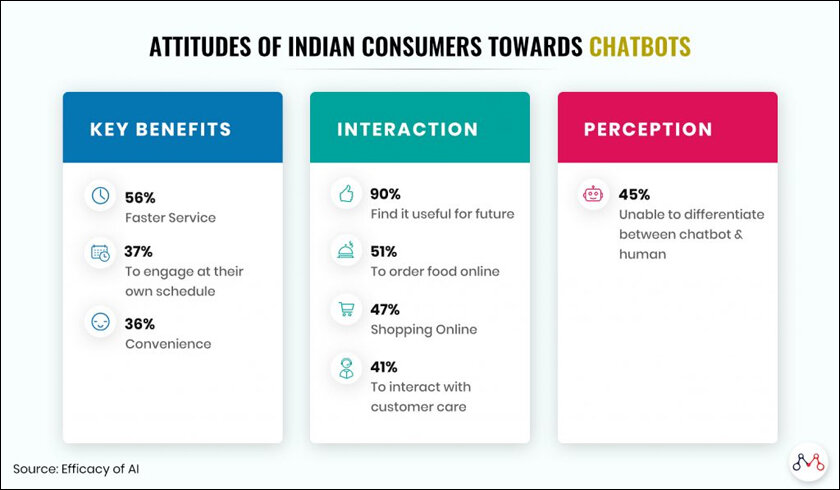
While the Indian chatbot industry is in its infancy, it is still a sizable $3.1 billion market and will keep growing with inclusion of AI and will be a market standard. It is estimated that 1.4 billion people are using chatbots, with the top 5- countries being the United States, India, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Brazil.
‘More than 30 million people have used the Indian government’s MyGov Corona Helpdesk WhatsApp chatbot since it debuted a year ago, according to Haptik, the conversational AI platform which developed the chatbot for the government’s health ministry. That makes the COVID-19 info provider the most-used WhatsApp chatbot ever.’
With the increasing pressure on rising costs for support, while both chatbot and virtual assistants or generative AI can be used, the level of investment would depend on the returns and the size of the business. For simple businesses for quick simple problems a basic rule based chatbot may be used, however, for complex sales generation aspects generative AI would be a better fit. With an industry worth $137 million, the utilization of the same along with the use of learning and AI is bound to grow to cater to the emerging markets in the future and put human potential to good use!
In case you missed:
- None Found









