Dinesh Elumalai explains the various species of artificial intelligence and how these affect human existence in an increasingly uncertain world
Most likely one of humanity‘s most complex and amazing inventions to date is artificial intelligence. And that ignores the fact that the field is still largely unexplored, which means that every incredible AI application we currently see only scratches the surface of the field. Even though this fact has been stated and reiterated numerous times, it is still difficult to fully understand the potential future impact of AI. This is because, even at this early stage in its development, AI is having a revolutionary impact on society.

People are paranoid about an impending AI takeover due to the technology‘s explosive growth and potent capabilities. Additionally, business leaders and the general public now believe that AI research has reached its pinnacle and that AI’s potential has been fully realized as a result of the transformation that AI has brought across various industries. The long road ahead for AI research will become clearer with a better understanding of the types of AI that are currently possible and those that already exist.
Various types of AI
The degree to which an AI system can mimic human capabilities is used as the criterion for categorizing the different types of AI because AI research aims to make machines mimic human-like functioning. Thus, among the various types of AI, a machine can be categorized under one of them depending on how versatile and effective it is compared to humans. A more advanced type of AI will be one that can perform more tasks that are similar to those performed by humans with an equivalent level of skill, while a less complex and less evolved type of AI will be one that has more limited functionality and performance.
While there are many different ways to categorize artificial intelligence, the two main classifications are based on the capabilities and the functionalities of the technology.
AI Based on Capabilities
- ANI – Artificial Narrow Intelligence
- AGI – Artificial General Intelligence
- ASI – Artificial Super Intelligence
AI Based on Functionality
- Reactive Machines
- Limited Memory
- Theory of Mind
- Self-aware
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
All currently existing artificial intelligence, including the most sophisticated and powerful AI ever developed, falls under this category. Artificial narrow intelligence is used to describe AI systems that can only carry out a single task on their own while possessing human-like abilities. These machines have a very small or restricted set of competencies because they are only capable of performing the tasks for which they have been programmed. These systems correspond to all reactive and limited memory AI, in accordance with the classification scheme mentioned above. Even the most advanced AI that learns new things through deep learning and machine learning is included in ANI.

Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
The stage of artificial intelligence development at which machines will be able to think and act similarly to how we do as humans is known as AGI, also known as strong AI.
Although strong AI has yet to be demonstrated, it is expected that we will soon be able to build machines that are as intelligent as humans.

The ability of an AI agent to think, perceive, comprehend, and act exactly like a human being is referred to as artificial general intelligence. These systems will be able to develop multiple competencies on their own, make connections between domains, and draw generalizations, significantly reducing training time. This will allow AI systems to mimic our ability to multitask, making them as capable as humans.
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
Artificial super intelligence is the stage of artificial intelligence where computers will be smarter than people. Currently, ASI is an imagined scenario from science fiction movies and books where machines have taken over the world.
If we take into account our current rate of advancement, I think that machines won’t be too far from reaching this stage.
The state of our world when more complex types of AI exist now is difficult to imagine. However, it is obvious that there is still a long way to go because AI development is still in its early stages compared to where it is expected to go. This suggests to those who are pessimistic about the future of AI that there is still time to ensure the safety of AI and that it is a little early to be worrying about the singularity. Furthermore, the fact that AI development is still in its infancy makes the future more exciting for those who are optimistic about it.
These are the various intelligence levels that a machine is capable of. So, what are the functionalities of the various AI subtypes? Some of these kinds of AI aren’t even currently conceivable from a scientific standpoint. Let’s examine each category in greater detail.
Reactive AI
The most basic type of AI is reactive AI, which is programmed to generate predictable results based on the input it receives. Reactive machines always respond the same way to the same situations every single time because they are incapable of learning actions or visualizing the past or future.

Although reactive AI represented a significant advancement in the field of artificial intelligence, these AIs are only capable of carrying out the tasks for which they were originally designed. As a result, they are already limited and susceptible to change. The next type of AI was constructed by scientists using this foundation.
Limited Memory AI
AI acquires practical knowledge by watching people or collecting data and learning from the past. This type of artificial intelligence (AI) combines pre-programmed information with historical, observational data to make predictions and perform difficult classification tasks. It is currently the most prevalent type of AI.
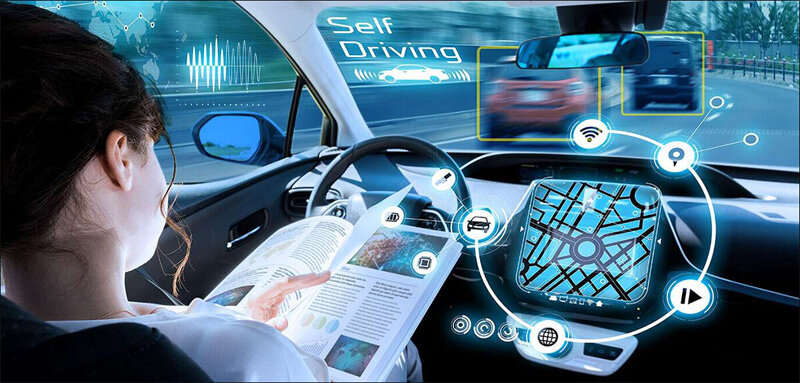
Autonomous vehicles, for instance, use AI with a constrained memory to track the speed and direction of other vehicles in order to “read the road” and make necessary adjustments. This way of understanding and interpreting incoming data makes them safer on the roads.
Despite what its name suggests, limited memory AI is still limited. The data that autonomous vehicles use is temporary and not kept in the vehicle permanently.
Theory of Mind AI
Do you want to have a meaningful conversation with a robotic person that has emotional intelligence and mimics human speech and appearance? Theory of mind AI will eventually achieve that.
This kind of AI will enable machines to make real decisions that are comparable to those made by people. Theory of mind AI will enable machines to comprehend and remember emotions, as well as modify their behavior in response to those emotions when interacting with humans.

Because human communication involves such a fluid process of shifting behavior based on quickly changing emotions, there are still a number of challenges to theory of mind AI. As we strive to build machines that are increasingly emotionally intelligent, it is challenging to mimic.
Having said that, we are moving forward. Professor Cynthia Breazeal’s robot head, code-named Kismet, is capable of recognizing emotional cues on human faces and recreating them on its own face. Sophia, a humanoid robot created by Hanson Robotics in Hong Kong, has the ability to recognize faces and can express her own emotions in response to interactions.
Self-aware AI
AI capable of self-awareness may be the most advanced kind. When machines are able to recognize their own emotions as well as the emotions of those around them, they will resemble humans in consciousness and intelligence. Additionally, this kind of AI will have desires, needs, and feelings.
This kind of AI will enable machines to recognize their own emotions and mental states. Other types of AI won’t be able to make inferences like “I’m feeling angry because someone cut me off in traffic,” but they will be able to.

This sophisticated AI has not yet been developed, and the necessary hardware and algorithms are not yet available.
Will we continue to develop AI’s abilities and produce a fifth type? In the next ten years, how far will we progress toward a theory of mind and a self-aware AI? Maybe a super-intelligent AI will be developed that even outperforms the level of human intelligence we currently possess?
Conclusion
We may be a long way from building intelligent machines that can solve every problem on their own. However, we should concentrate our efforts on comprehending how a machine can train and learn on its own and have the capacity to draw conclusions from the past.
I sincerely hope this article has aided in your comprehension of the various forms of artificial intelligence.
Have you got any inquiries about this article? Do mention it in the comments section below.









2 Comments
It’s becoming clear that with all the brain and consciousness theories out there, the proof will be in the pudding. By this I mean, can any particular theory be used to create a human adult level conscious machine. My bet is on the late Gerald Edelman’s Extended Theory of Neuronal Group Selection. The lead group in robotics based on this theory is the Neurorobotics Lab at UC at Irvine. Dr. Edelman distinguished between primary consciousness, which came first in evolution, and that humans share with other conscious animals, and higher order consciousness, which came to only humans with the acquisition of language. A machine with primary consciousness will probably have to come first.
What I find special about the TNGS is the Darwin series of automata created at the Neurosciences Institute by Dr. Edelman and his colleagues in the 1990’s and 2000’s. These machines perform in the real world, not in a restricted simulated world, and display convincing physical behavior indicative of higher psychological functions necessary for consciousness, such as perceptual categorization, memory, and learning. They are based on realistic models of the parts of the biological brain that the theory claims subserve these functions. The extended TNGS allows for the emergence of consciousness based only on further evolutionary development of the brain areas responsible for these functions, in a parsimonious way. No other research I’ve encountered is anywhere near as convincing.
I post because on almost every video and article about the brain and consciousness that I encounter, the attitude seems to be that we still know next to nothing about how the brain and consciousness work; that there’s lots of data but no unifying theory. I believe the extended TNGS is that theory. My motivation is to keep that theory in front of the public. And obviously, I consider it the route to a truly conscious machine, primary and higher-order.
My advice to people who want to create a conscious machine is to seriously ground themselves in the extended TNGS and the Darwin automata first, and proceed from there, by applying to Jeff Krichmar’s lab at UC Irvine, possibly. Dr. Edelman’s roadmap to a conscious machine is at https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.10461
Nice post!