For all those looking to figure out the complicated infrastructure, jargon and usability, Felista Gor provides a 101 on cloud migration
The cloud has become synonymous with progress in the business world. It allows companies to get closer to their customers, focuses their staff on innovation, cut down on costs and so much more. This article will set you on the right path to migrating your workloads, applications, and processes to the cloud.
What is cloud migration?
Cloud migration is the process of transferring applications, databases, digital assets, and other IT resources wholly or partially to a cloud computing environment. It also entails moving from one cloud to another.
What are the benefits of cloud migration?
Organizations today consider cloud migration as an overly complex solution, however, it has its own benefits that are unique and important.
1. Scalability
Cloud enables organizations to improve on scalability. The scaling process is done automatically in a process called auto-scaling. Scalability allows organizations to instantaneously add and remove resources on a need basis or when matching demand.
2. Cost saving
Cloud gives enterprises the ability to only pay for resources they use. This capability gives enterprises access to resources that would cost too much time and money to purchase and maintain. The traditional IT approach required an enterprise to buy the hardware upfront and keep the infrastructure up and running. With the cloud, that is all done instantly by the cloud provider.
3. Less maintenance
Maintenance of IT infrastructure is a full-time job that sometimes overwhelms employees. Cloud migration takes away the tedious task by ensuring cloud providers take care of all the infrastructure and maintenance and allow the IT team to focus on driving core business outcomes.
Cloud migration process
These processes are different based on factors like application maturity, migration strategy, and infrastructure complexity. However, every migration will include the following basic steps.
- Planning: You should have apparent reasons and strategies before getting started with cloud migration. Start by assessing your current environment by calculating your cloud server requirements based on current application resource requirements. This will help you avoid buying more than you need. At this step, you need expertise and resources from a specialist. An application performance management solution is important as it supplies a complete and real-time overview of your environment and its dependencies and suggests proper strategies.
- Choosing your cloud environment: Now that you have the visibility you need, you can choose the cloud model you want to adopt. The chosen model depends on what best serves your current and future needs.
- Migrating your apps and data: Proper planning will ensure the smooth migration of your applications and data to the cloud. Still, keep in mind potential risks like security concerns and ensure necessary strategies are set in place. Be sure to use app performance management solution to baseline pre-migration performance before taking the next steps.
- Validating post-move success: A cloud migration process is not successful unless there is evidence to show the same. Compare a pre and post-move application performance analysis from both a technical and business perspective to gauge the results.
Types of cloud migration strategies
The first thing to consider when migrating to the cloud is the strategy the company wants to adopt. Determining the type that matches your organization’s goals and needs is the first step to a successful migration.
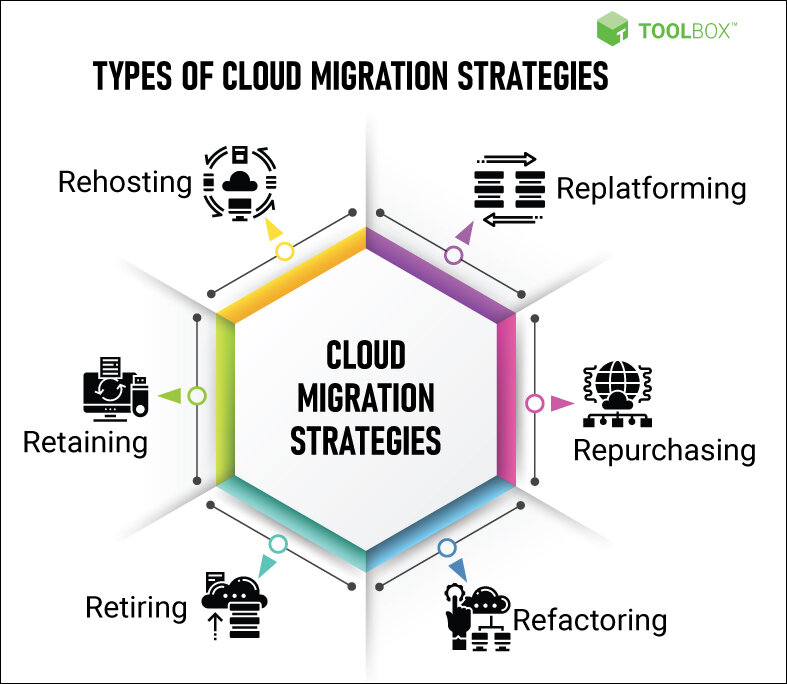
1. Rehosting
It involves shifting data and applications from an on-premise data center to a cloud service. Organizations are encouraged to start with the simplest items with few dependencies, low constraints, and low business impact and finalize with the most complex items as maturity increases.
2. Replatforming
This is moving to a whole new cloud-based operating system. Organizations that conduct re-platforming want their core competencies to be scalable, robust, and elastic. It is also for those looking to get into containers or microservice architectures. Re-platforming involves replacing the application at the code level to make it cloud-native. The application becomes easier to maintain and update thus boosting the speed of change across all aspects of the business.
3. Repurchasing
This is a cloud migration strategy where you change the proprietary application in use for the new cloud-based platform or service. For example, you may choose to switch from your legacy CRM (Customer Relationship Management) to a new SaaS (Software as a Service) CRM that meets the organization’s goals better.
4. Refactoring
With re-factoring, you replicate legacy applications whole in the cloud environment. This approach focuses on applications that benefit the most on the cloud platform. Re-factor enables you to save time by minimizing spending on things you will not need once you are on the cloud. For example, switching from Oracle WebLogic to cloud-native JBoss can cut costs.
5. Retaining
Sometimes it is easier to retain your current situation and not make any changes. You can keep some components of your IT infrastructure such as databases and stand-alone workloads and create a hybrid infrastructure where some workloads are hosted on the cloud while others are kept on premises.
6. Retiring
Situations may compel you to retire a legacy system and move your users to a system that is already in place. This often requires that you archive unnecessary systems by replacing their functionality with other services or components in the cloud.
What are some challenges of cloud migration?
Every cloud migration is different meaning each business faces different challenges. Below are some common challenges that businesses face during the cloud migration process.
1. Skill gap
The skills required to manage an on-premise data center are different from those of managing a cloud environment. Ideally, you will want to reskill your existing team. If this is not feasible, you will need to outsource specialists or reach out to managed service providers to oversee daily operations.
2. Legacy assets
Traditional IT infrastructure and data centers will need to be decommissioned. As you plan your migration, consider including contract penalties, building leases, or hardware removal costs in your plan.
3. Disruption
Sometimes it is inevitable to encounter challenges when migrating to the cloud even with the best plan. These challenges may lead to potential data loss, outages, and performance degradation. Ensure that you plan the migration during low-traffic business periods and set in place measures to minimize disruption.
Conclusion
Cloud migration is a tall order. Your migration strategy should be robust and in line with the business goals. Cloud migration should be done with agility to ensure business continuity. This guide can help you hit the ground running in your cloud migration journey.
In case you missed:
- None Found










1 Comment
Great post