The cloud ecosystem supports many of the consumer services most people use daily and is increasingly adopted by financial institutions to reduce cost or meet other business needs.
What is cloud banking?
Cloud banking relates to the use of online delivered services that enable customers access financial accounts from their licensed or even unlicensed devices such as tablets, mobile phones & personal computer just by using internet. Most of other cloud computing services are based on a remote access, including physical servers, virtual servers and data centers as well SaaS etc.

Cloud banking has other benefits, which aside from making it easier and more accessible than traditional banks also provides customers with options to file many things online. This means cloud-based banking services are used to facilitate transaction whenever a customer uses the pay-per-view game from home, rideshare app or any other casinos who offer innovative digital gaming experience primarily by virtue of their unique system built for microservices.
The cloud ecosystem supports many of the consumer services most people use daily and is increasingly adopted by financial institutions to reduce cost or meet other business needs. Being the engine behind applications that improve telework to possessing such a high compute power required for AI, ML and Cloud in banks around the world: Applications of Internet of Things (IoT)
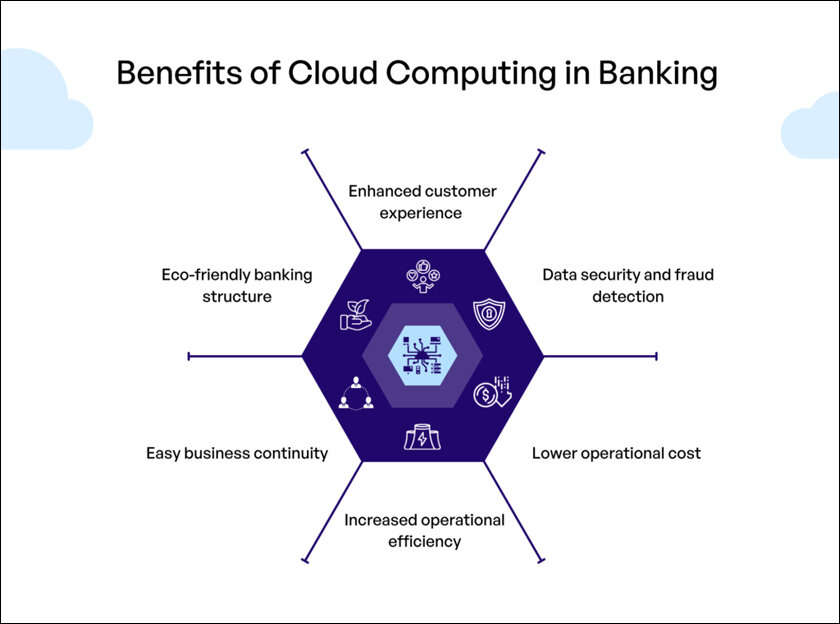
Importance of Cloud Banking
Cloud banking has meant a real transformation for consumers, who see how their daily activities such as shopping, or transportation are much easier. Think about you are buying the grocery and had to pick up your kids from school. But until cloud banking became a reality, that could mean stops in several disparate places to carry out each of these processes. But these can now all be done with a headache on just the smartphone and your bank’s internet banking app.
Consumer aside, the power of cloud banking is not limited to consuming alone. The banking industry, however, is increasingly using the technology to enhance data protection of customer information, develop more original products and deploy AI & ML technologies for automation of repetitive tasks. Indeed, the finance industry has been leading- even outpacing other sectors in this transition: it made up to 16% of global cloud spend due mainly to increased momentum on moving applications and resource-intensive workloads into AWS at (vs other hyperscale) financial institutions.

Advantages for financial institutions in the cloud banking
While financial institutions turn to the cloud ever more frequently and discover that it can contribute decisively not only to making better products and services available for customers as part of their digital transformation, several additional advantages are becoming clearer.
Reduced costs
This has driven savings for banks in data storage layout and handling of data analysis with the cloud today less costly than running workloads on-site. This is a big area to find value, because banks keep detailed financial records by law on all people account at the bank. Cloud banking enables financial services organizations to move from a traditional on-premises data storage model with an up-front cost, into more flexible pay-as-you-go options that can be scaled as necessary.
Improved data security and compliance
Since banks hold some of the most important information and assets for customers, it is not unusual that they are targeted by hacking or fraud attempts; but moving these financial services to the cloud has made them safer. Current cloud banking solutions compile various layers of security protocols to ensure that no individual or organization has access to sensitive customer data. Using cloud banking solutions also ensures that banks remain regulatory compliant and adhere with the dynamic set of government regulations vigilance over their industry. Lastly, DR capabilities that come with many cloud offerings provide financial institutions a way to quickly recover from potential data breaches or large-scale outages.

Increased AI capabilities
The Cloud has enabled banking systems to embrace AI (on a per-use basis or full mode across workloads) Take, for instance data on customers and development of products. If a bank keeps their customer data in the cloud, AI algorithms could be working on it all of the time to understand how customers behave therefore inform future product designs and features. An example is that AI chatbots and virtual agents are improving customer service, replacing call centers in the CRM space to help new customers sign up for a bank account or transfer money between accounts of even apply for credit cards.
Quicker release of new services
The fact is, that Cloud banking space is extremely dynamic and fast-paced where new applications /services are being built every day. In this new cloud-centric model, a lot of the capabilities are plug-and-play — that is to say many components for building bank services in the cloud have already been developed so they can be put together quickly by banks as things change. If an incumbent bank that is in the process of adopting cloud unravels a customer pain-point, then most likely there’s probably some sort on-the-shelf product waiting to be added and elevate user experience instantaneously.
How does cloud banking work?
In the earlier days, cloud banking mostly was a term associated with offering financial services to be served by banks sitting remotely from their customer instead going in person at physical location. This is changing as the industry has matured, with banks now using cloud to implement solutions across infrastructure and banking operations — particularly data storage & processing.
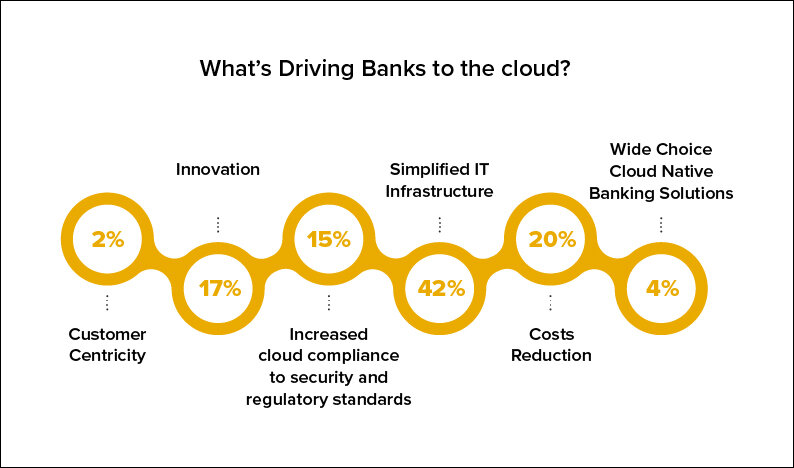
The Evolution of the Cloud Bank
The inception of the 2000s saw fast internet speeds and smartphones as innovation that would trigger a digital evolution in banking. But a sector so weighed down by the costs, and confines of bricks and mortar infrastructure was changing. After that, as we know, banks began to provide more and more services via the Internet. Despite initial fears about data privacy and encryption, they began to trust the space more, allowing those barriers for people like me to disappear.
In the latter part of this new millennium, customers didn’t think twice about going online to check their accounts 24/7 — and from at least one device. When security became a much stronger feature of public cloud offerings than it had been previously, then banks would indeed start to connect their servers and databases via the internet not anymore in an on-premises data center. This effectively turned all banks into customers for solutions in both private clouds and public clouds, creating the cloud banking era where CSPs ( cloud service providers) compete in security/technology/adaptability to match what banks need.
Financial institutions must strike the right balance between customer demand for cutting-edge applications & services and meeting rigorous regulatory requirements. Cost also plays a significant role in shaping cloud strategy. But among the most vital decisions they face is whether to deploy in a public or private cloud
We believe you all would have got some idea about what cloud banking is and how it is being used, for more information about cloud banking, check our future contents will give insight about the difference of public & private cloud, and examples of cloud banking.