With companies reclaiming control via cloud repatriation, models that involve private cloud, either as is or in tandem with public cloud, meet the needs of organizations in a cost-effective, agile, and controlled manner, offering immense peace of mind.
Private cloud is making a comeback, all thanks to the generative AI gold rush. AI data leak fears and cost uncertainties have CIOs rethinking future cloud strategies. Today, the seemingly passé private cloud, either hosted by a partner or an on-premises solution, is getting a second look — and then some. Since they boast a single-tenant cloud infrastructure, they are ideal settings for companies and industries with sensitive data, including healthcare, finance, and government. Despite businesses moving towards private cloud adoption at record rates, some are still reluctant to take the leap. Here are six ways private cloud adoption can create a host of benefits for and add immense value to the enterprise.
1. Private cloud storage: Secure storage is one of the top-selling points when it comes to private cloud. It allows companies working in sensitive fields with sensitive data, like financial institutions, to protect and control who has access to it. For instance, only those team members or administrators who have been granted the necessary permissions can access and interact with customer data via a private connection like a VPN (virtual private network).
2. Compliance and data privacy requirements: Some industries have very sensitive data or possess very stringent compliance standards, which could dictate security. Due to its limited access, a private business cloud environment can meet the compliance standards required by law. It is also perfect for businesses and companies that have regulatory compliance or data protection. For instance, healthcare companies need to protect sensitive patient health information from being disclosed or hacked. Private cloud environments allow such healthcare organisations to employ physical and administrative controls designed to store and safeguard.
Basically, one must be a part of the organisation to be privy to the internal network if they were to try and pierce through its firewall. Quite simply, since the private cloud is, well, private, it is not as easily accessible as the public cloud, as those who do not have access will not even know that it even exists.
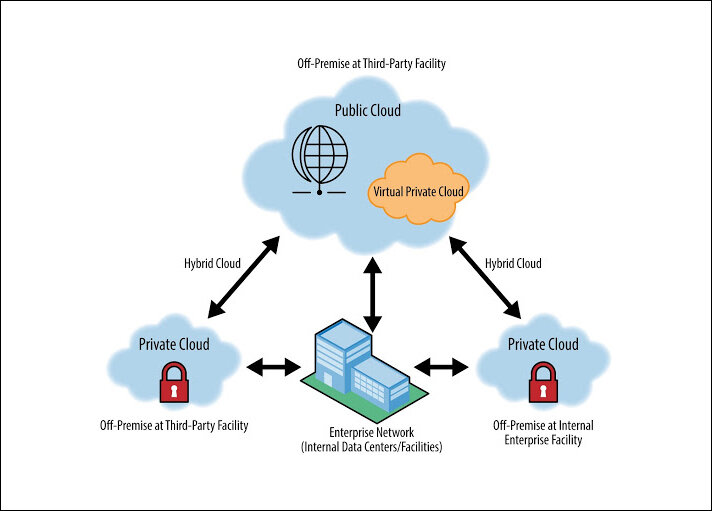
3. Hybrid multi-cloud strategy: Contrary to what many believe, private cloud plays a crucial role in a hybrid multi-cloud environment. For instance, a bank can employ a hybrid cloud strategy and use a public cloud to test and develop new applications on its mobile app, like a customer loyalty program. At the same time, it can store sensitive customer information on a private cloud, thus preserving confidentiality. Security and scalability go hand-in-hand with this strategy, giving organizations and businesses the agility and control to choose the best cloud environment for every particular workload. However, the security bit cannot be maintained without the use of the private cloud.
4. Enabling application modernization: Application modernization is when an organization updates its existing applications to a cloud-first model. Also known as legacy modernization, the process ensures a smooth transition of an organization’s on-premises applications to a private, public, or hybrid cloud. Today, an increasing number of companies and businesses are using private clouds to modernize legacy applications as part of their application modernization journey. Since one can customize private clouds to handle sensitive data and workloads, it allows and ensures a smooth and secure transition to the cloud.
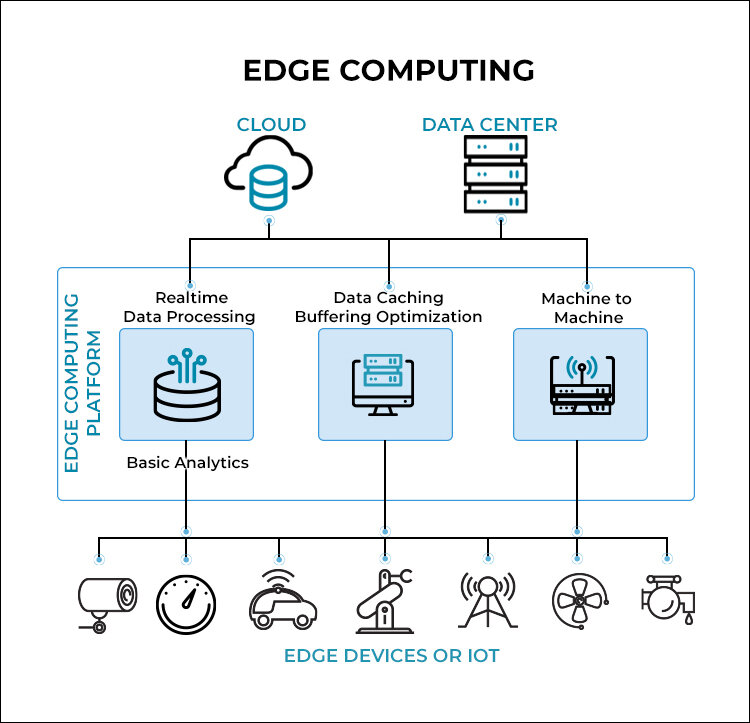
5. Edge computing: Edge computing is a decentralized approach that brings computing power and storage closer to where data is created, or its “edge.” Private cloud infrastructure can be deployed at this “edge,” allowing sensitive data to be processed locally. For instance, companies can leverage IoT and employ smart grids to monitor energy use better and manage energy consumption. Thanks to real-time visibility, energy companies and other enterprises can strike new deals and even look to increase the amount of green energy consumed.
6. Cost control: In the past, private cloud infrastructure was built specifically and mainly for an organization, thus resulting in a lot of upfront costs. However, this ensures that there are no surprises and that the organization will know what their monthly bill looks like. While scaling might take a lot more planning, the fact is that such a cloud environment can be budgeted for accordingly. That is why organizations that need bursts of resources often end up opting for a hybrid cloud model, as they can use a private cloud and appropriately budget their expected processing needs. After that, they can spin up a public cloud for deployment to quickly scale up and down. In fact, private cloud services for on-demand businesses have gained immense popularity in the last three years and have brought significant improvements.
Another thing to note is that organizations today are starting to leverage the capabilities of generative AI across cloud environments, including private cloud. For instance, generative AI models can significantly strengthen cloud security by analysing historical data and identifying anomalies and patterns in private cloud infrastructure, thus revealing threats, if any, in real time. With companies reclaiming control via cloud repatriation, models that involve private cloud, either as is or in tandem with public cloud, meet the needs of organizations in a cost-effective, agile, and controlled manner, offering immense peace of mind.
In case you missed:
- Has Private Cloud Made Its Comeback?
- All About Cybersecurity-as-a-Service
- The Cloud Cost Conundrum: Is Cloud FinOps the Answer?
- The Rise Of Agentic Cloud – Reshaping Cloud Infrastructure In 2026
- The Rise Of Cloud WAN and SD-WAN: Network For The AI Era
- The Good Samaritan: A Complete Guide To Ethical Hacking
- India’s DPDP Act: Data Privacy Or Data Surveillance?
- All About AI Prompt Injection Attacks
- Hiding In The Dark: Navigating The Threat Of Shadow AI
- All About Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETS)









