Dinesh Elumalai explains the trend of on-site data centers shifting over to the virtual world and how this will impel the future
Cloud computing advancements and increased demand for flexible IT (Information Technology) solutions have resulted in innovative technologies that have transformed the traditional data center over the last decade.
As server virtualization has become more common, many businesses have shifted from physical n-site data centers to virtualized data center solutions.
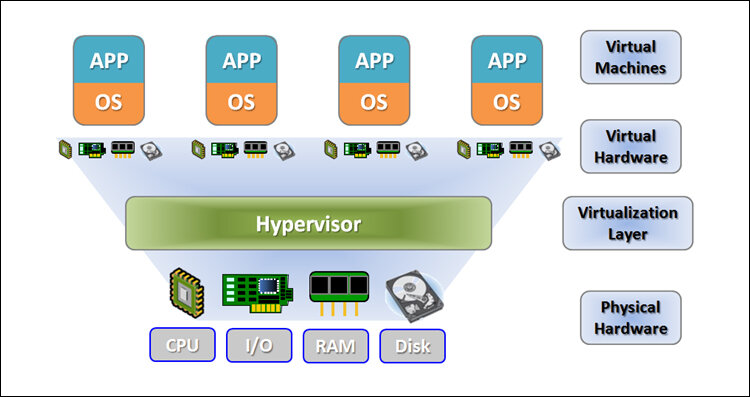
How does Data Center Virtualization work?
Data center virtualization is the conversion of physical data centers into digital data centers via a cloud software platform, allowing businesses to access information and applications remotely.
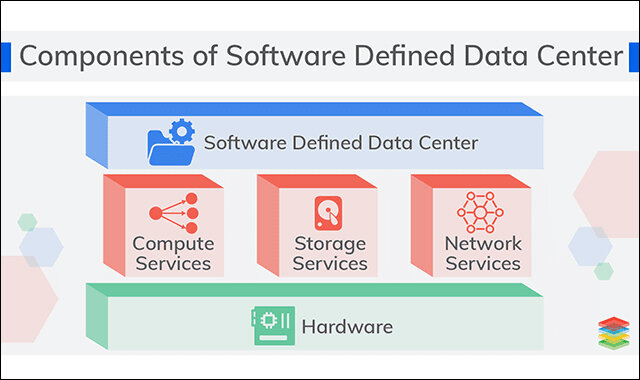
A virtual server, also known as a software-defined data center (SDDC), is created from traditional, physical servers in a virtualized data center. With the assistance of a hypervisor, this process abstracts physical hardware by imitating its processors, operating system, and other resources.
A hypervisor (also known as a virtual machine monitor, VMM, or virtualizer) is a piece of software that creates and manages virtual machines. It treats CPU, memory, and storage as a pool of resources that can be easily reallocated between existing virtual machines or to new ones.
Sify Technologies – Data Center Services
What is the difference and how they are related – Cloud and Virtualization
It is easy to mix up virtualization and cloud computing. They are, however, quite different but also remarkably similar. Simply put, virtualization is a technology that creates multiple simulated environments or dedicated resources from a physical hardware system, whereas the cloud is an environment in which scalable resources are abstracted and shared across a network.
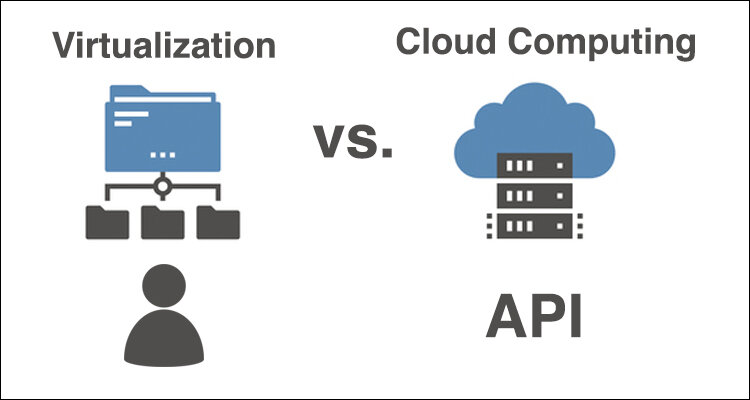
Clouds are typically built to support cloud computing, which is a set of principles and approaches for providing compute, network, and storage infrastructure resources, platforms, and applications to users on-demand across any network. Cloud computing enables different departments (via private cloud) or businesses (via public cloud) to access a single pool of automatically provisioned resources, whereas virtualization can make one resource act like many.
Virtualization and cloud computing are frequently used in tandem to provide a variety of services. Virtualized data center platforms can be managed from a single physical location (private cloud) or from a remote third-party location (public cloud), or from a combination of the two (hybrid cloud).
Private or in-house teams deploy, manage, and protect on-site virtualized servers. Alternatively, third-party virtualized servers are managed in remote data centers by a service provider that provides cloud solutions to a wide range of businesses.
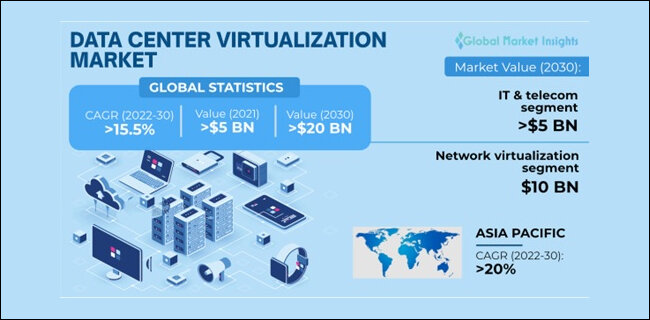
Data Center Virtualization Market
Virtualization of Data Centers The market exceeded USD 5 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of more than 15.5% between 2022 and 2030. The growing awareness of the benefits of cloud-based data storage, as well as consumer preference for digital transformation, will drive industry growth.
An increase in data center energy consumption, particularly in Europe, is expected to drive market demand. Data center virtualization replaces traditional physical servers and other related equipment with virtualization software and cloud computing technology.
The growing emphasis of BFSI enterprises on transferring data to cloud platforms to improve business agility is expected to drive data center virtualization market growth. Companies are primarily forming strategic growth partnerships with public and private organizations in a variety of industries that require data digitization. They are also working to improve their flexibility and dependability by incorporating data center infrastructure.
There is a high demand for low-cost data storage solutions
By 2030, the data center network virtualization market is expected to be worth USD 10 billion. The segmental growth can be attributed to rising efforts to reduce data center operational costs, which can be accomplished through network virtualization, which groups physical networks to operate as a single or multiple independent networks known as virtual networks, thereby assisting in cost-efficient data storage.
By 2030, the managed services segment is expected to generate nearly USD 2 billion. The increasing need for specialised and dedicated day-to-day operations to run at peak efficiency is expected to fuel managed service growth, propelling the overall data center virtualization market expansion.
Advantages of Data Center Virtualization
Businesses seeking increased profitability or scalability can benefit from data center virtualization in a variety of strategic and technological ways. Let’s now discuss the merits of the Data Center Virtualization.

Scalability
In comparison to physical servers, which necessitate extensive and sometimes costly sourcing and time management, virtual data centers are easier, faster, and less expensive to set up. Any company experiencing rapid growth should consider implementing a virtualized data center.
It is also a good fit for businesses that see seasonal increases in business activity. Virtualized memory, processing power, and storage can be added at a lower cost and in a shorter timeframe than purchasing and installing components on a physical machine during peak times. Similarly, as demand declines, virtual resources can be reduced to eliminate unnecessary costs. These are all impossible with metal servers.
Mobility of Data
Prior to virtualization, everything from routine tasks and daily interactions to in-depth analytics and data storage occurred at the server level, which meant they could only be accessed from a single location.
Virtualized resources can be accessed when and where they are needed with a strong enough internet connection. Employees, for example, can access data, applications, and services from remote locations, significantly increasing productivity outside the office.
Furthermore, virtualized servers enable versatile collaboration and increase sharing opportunities by utilising cloud-based applications such as video conferencing, word processing, and other content creation tools.
Savings on Expenses
Physical servers, which are typically outsourced to third-party providers, are always associated with extensive management and maintenance. However, they will not be an issue in a virtual data center. Unlike physical servers, virtual servers are frequently offered as pay-as-you-go subscriptions, which means that businesses only pay for what they use.
In contrast, whether physical servers are used or not, companies must bear the costs of management and maintenance. In addition, the additional functionality provided by virtualized data centers can reduce other business expenses such as travel costs.
We leave you with these insights on Data Center Virtualization. If you have any thoughts or clarifications, would request you to post your comments below.
In case you missed:
- None Found









