Edge computing is revolutionizing data processing by bringing computation closer to the source, enabling real-time decision-making across industries.
Edge computing is a revolutionary technology that is reshaping how data is processed and used across various industries. By bringing data processing closer to where the information is being generated-whether it’s IoT devices, smartphones, or sensors-edge computing significantly reduces the latency, enhances performance, and supports real-time decision-making.

It is not just a case of faster transmission of data but it is about smarter and more autonomous systems that can react instantly. This article covers the basics of edge computing-its relationship with data centers and its importance for instant insights and smart decisions.
Edge refers to a distributed framework bringing computation and storage as close as possible to data sources-decreasing delays and increasing speed and processing power for data-intensive applications.
Traditionally, cloud computing processes data at centralized data centers. Edge does so at the network edge-the generation point-permitting real-time analytics and decision-making critical for applications needing instant responses (autonomous vehicles, smart cities, IoT, etc.).
Role of Edge Computing in Data Processing
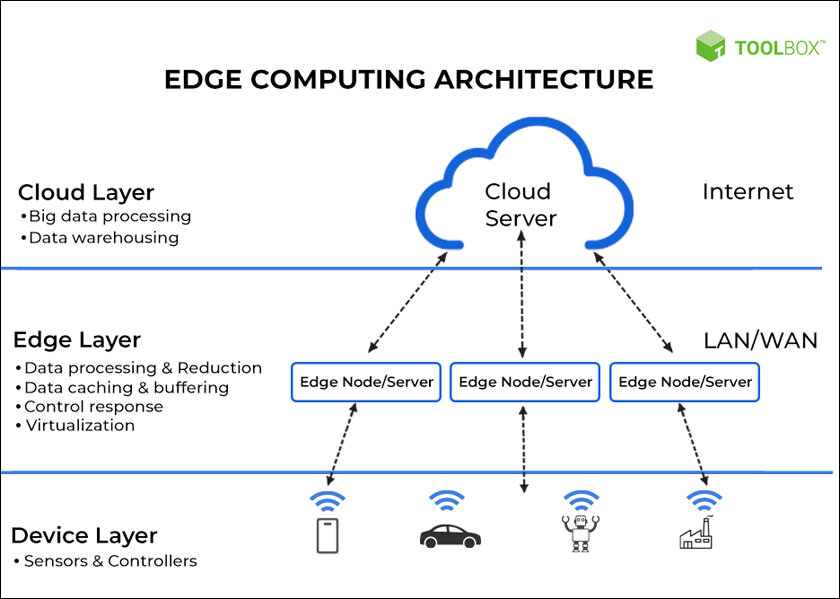
Edge computing plays the central role in modern data processing-the growing number of IoT devices and applications illustrates this. It tackles bandwidth bottlenecks, latency, and connectivity issues in centralized cloud computing. Local or near-source data processing by edge computing minimizes the amount of data that moves through the network from edge to the central data center. This localized processing capability is an essential component of time-sensitive applications that require immediate processing and prompt incidents.
The effect? More efficient operations, less latency, better user experiences.
Data Centers and Edge Computing

Data centers, seen as the center of IT infrastructure, are evolving to support edge computing architectures. In this structure, they remain the focal point but are more distributed; they act as anchor points for the edge computing framework, offering backup, storage, and advanced processing capabilities that might not be available at the edge. Such a hybrid approach assures that real-time processing takes place at the edge while data centers can deal with more sophisticated analysis, historical aggregation, and long-term storage. This combination of edge computing and data centers allows a more flexible and scalable as well as efficient infrastructure for computing.
Perks of Using Data Centers for Edge Computing
Incorporating data centers into edge computing offers:
- Security: Centralized data centers may provide advanced security measures that ensure the data processed in the edge is securely backed up and shielded against cybersecurity threats.
- Advanced Processing: While edge computing is tasked with real-time processing, data centers tend to tackle more complex analytics, combining the data from multiple edge locations in order to get in-depth insights.
- Reliability: Through redundant and failover solutions, data centers can keep running even if edge devices have issues.
- Scalability: Data centers provide the necessary infrastructure to scale edge computing solutions-accommodating the growing amount of data generated by IoT devices.
Challenges in Implementing Edge Computing in Data Centers

- Data Synchronization: Ensuring consistent data across central data centers and edge devices will need futuristic synchronization mechanisms.
- Complexity: Handling infrastructure that incorporates both centralized data centers as well as the distributed nodes at the edge leads to an extra level of complexity in account deployment, management, and maintenance.
- Security: Extending the network edge makes it more vulnerable and increases the attack surfaces.
- Cost: The initial installation and maintenance of an edge computing structure might be expensive for organizations that need to retrofit their current data centers to incorporate edge computing capabilities.
Real-Time Decision-Making with Edge Computing
Applications across Industries
The following are potential applications of real-time decision-making powered by edge computing:
1. Healthcare: Continuous monitoring of patients’ vital signs, enabling immediate interventions
2. Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance through real-time identification of machinery issues, preventing costly downtimes
3. Retail: Personalized shopping experiences tailored to individual customers’ behaviors and preferences in real time
4. Smart Cities: Dynamic traffic management systems that adjust to changing conditions
5. Autonomous Vehicles: Instantaneous decision-making for navigation and obstacle avoidance, ensuring safety and efficiency
These examples merely scratch the surface of the vast potential that edge computing holds for real-time decision intelligence across sectors.
Conclusion
The synergy between edge computing and data centers will unveil new dimensions of efficiency and agility in processing vast amounts of data, revolutionizing how we interact with technology in our daily lives and work environments. The journey toward more responsive and intelligent systems is well underway, promising an exciting future that seamlessly blends the physical and digital worlds.
In case you missed:
- Understanding Data Residency
- 7 Sustainable Practices to Reduce IT’s Environmental Impact
- Equipping Businesses with AI: Strategies and Best Practices
- Zero Trust Security
- How to Secure Your DevOps Pipelines?
- Essential Skills You Need to Thrive in an AI-Driven Workplace
- All about Ransomware
- Balancing the Scales: AI Evolution vs Ethics
- Supply Chain Attacks: Recognizing and Preventing Risks from Third Parties
- How to Implement Multi-Factor Authentication for Enhanced Security?